Gray Zone and Restriction of Freedom Paralyze the German iGaming Market [Analysis]
Online gambling in Germany has been a source of controversy for many years. The introduction of a treaty aimed at regulating the market has paradoxically contributed to the creation of a sort of “wild west,” leading to an increase in the gray market and a restriction of players’ freedom. In this article, we explore the paradoxes present in the German market, as well as the consequences and dangers resulting from irresponsible regulatory policies.

For years, the online gambling market in Germany was unregulated, creating chaotic conditions for both players and operators. The lack of clear regulations and frequent legislative changes have made the market difficult to control.
The Great Potential of Germany
Germany is a country where the online gambling industry still holds considerable potential. According to a Hootsuite report from 2022, the 83-million-strong country has nearly 59 million mobile internet users, accounting for about 87.4% of the total population.
95.4% of internet users are aged between 16 and 64. A significant 83.8% own a laptop or desktop computer, while 52.7% own a tablet. Hootsuite also reported that 78.81 million people were regular internet users, representing 94% of the entire population.
This highlights the great potential for iGaming in Germany. Despite being such a technologically advanced country, it continues to struggle with issues related to gambling. The German iGaming market was valued at €2.8 billion in 2021. According to a report published by Hootsuite in 2022, the industry was forecasted to grow to €3.3 billion by 2024.

A study conducted by Goldmedia found that German players most frequently engaged in casino games and online betting. According to the mentioned source, 12% of respondents played at online casinos daily, and 32% played weekly. The introduction of regulations concerning online gambling in Germany, including stake limits on slot machines and advertising restrictions, has significantly influenced the shape of the casino market in Germany.
Online casinos constitute a significant part of the market, thanks to the increasing internet access and a large number of young adults who are the main users of online services. The German online casino market is currently in a phase of dynamic development, but it still faces significant challenges following the introduction of the 2021 treaty.
Sports betting also enjoys considerable interest. According to the Goldmedia report, 15% of players place bets daily and 29% weekly. Unfortunately for the industry, the regulations being implemented in Germany mean that players still gamble, but not necessarily with legal operators.
Does it have to be this way? Definitely not, as explained further in the article, where you will find opinions from experts involved in the German online gambling market.
Sports Betting in Germany
According to Global Data, Germany is the fifth-largest sports betting market in the world. In 2021, the value of the sports betting market in Germany was $1.9 billion, accounting for 1% of the global market. Germany represents 8% of the European market’s value.

At the beginning of 2020, the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic had a huge impact on the sports betting sector, as most outdoor venues were closed, and people were forced to spend most of their time at home. Due to the lack of sporting events for most of the year, gambling activities practically came to a halt. As a result, the value of the sports betting market in Germany dropped by 19% in 2020, a decrease of $0.4 billion.
Betting on football, basketball, and horse racing are among the most popular types of bets in Germany. The sports betting market in Germany experienced significant growth after the COVID-19 pandemic, as restrictions were eased and interest in sports betting increased. After the easing of restrictions, the sector saw a rebound in demand, and the German sports betting market grew by 14% in 2021, increasing the market’s value by $0.23 billion.
The German online gambling market is one of the largest in Europe, with the number of players using legal gambling sites estimated at several million. The regulations introduced in recent years aimed to increase the attractiveness of legal offers, but paradoxically, they have contributed to increased competition from illegal operators.
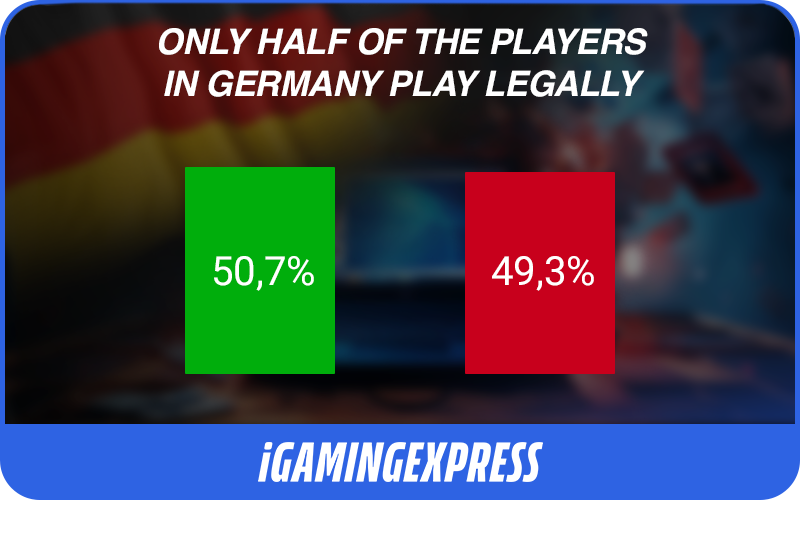
In Germany, the number of iGaming players is significant and continues to grow. However, the gray market remains a problem. According to the latest estimates, the German iGaming market includes a large number of active users, but only half of them play fully legally. In March 2023, it was found that the rate of player migration towards the regulated online space was 50.7%. One reason for the high rate of players with illegal operators is the introduction of the treaty, which significantly affects the freedom of iGaming enthusiasts.
The Treaty That Was Supposed to Change Everything but Turned Out to Be a Dud
After years of complete freedom and lack of any regulations, a new treaty was introduced in July 2021 to bring order to the gambling market in Germany. Before its implementation, the legal gambling market was largely suspended, leading to the growth of a gray market where players used the services of illegal operators. This treaty aimed to regulate the online gambling market by introducing new rules and standards.
In theory, this treaty was supposed to bring order and transparency to the gambling market. In practice, however, the changes were far from ideal. On one hand, the introduction of licenses for operators was a step in the right direction, aiming to increase market control and protect players from unfair practices. Operators had to meet certain requirements to obtain a license, ensuring the safety and transparency of their operations. On the other hand, the new regulations introduced numerous restrictions that discouraged many players and operators.
One of the key elements of the new treaty was the numerous restrictions aimed at protecting players. Limits on stakes, playing time, and deposits were introduced to reduce the risk of gambling addiction. Each player could only bet up to a specified amount per hour and spend a limited amount of time on gambling platforms. Additionally, games with jackpots were banned, as they were considered particularly risky due to the high sums to be won, which could lead to impulsive decisions and significant financial losses. Although the intentions were good, many players found these restrictions excessive and limiting their freedom.
Another controversial element of the new regulations was the ban on online gambling advertising, which could only be shown at night, between 9:00 PM and 6:00 AM. This was intended to reduce exposure to gambling, especially among younger age groups, which are particularly susceptible to addiction. Operators had to adjust their marketing strategies, further complicating their operations and affecting their revenues. This ban was criticized by both operators and some players, who felt that such restrictions were excessive and disproportionate to the goal they were supposed to achieve.

The introduction of the new treaty also impacted the technological aspect of the gambling market’s operations. Operators had to implement new monitoring and reporting systems to ensure compliance with the new regulations. This required significant investments and adjustments, which was not easy, especially for smaller companies. Large corporations had greater adaptive capabilities, but for smaller entities, the new requirements could pose significant challenges and the risk of ceasing operations.
It is also important to consider the social context of the new regulations. The German public was divided on the new rules. Supporters of the treaty argued that protecting against gambling addiction was a priority and that the new regulations were necessary to ensure players’ safety. Critics, however, claimed that the regulations were too restrictive and that excessive regulation could lead to a return to using illegal platforms, ultimately having the opposite effect of what was intended.
The 2021 treaty introducing regulations in the online gambling market in Germany was a step towards increasing control and safety in this sector. Although its introduction aimed to organize the market and protect players, it was also met with criticism for its overly restrictive approach. Many players feel that the regulations significantly limit their freedom.
Consequences of the Treaty
Before the 2021 Gambling Treaty was introduced, during the subsequent transition period, there was already a huge gray market. It primarily consisted of operators seeking to legalize their activities in the country. Some of them gave up, while others persisted, losing their market share.
According to Willem van Oort, founder of Gaming in Germany, it is not surprising that if only betting and online slot machines are allowed, there will always be players looking for other products, such as online roulette, live games, and similar options. Our expert also points out the issue of gambling taxation.
“The German tax rate contributes to a very uncompetitive product. Still, players generally prefer to make use of licensed offerings. This means that not everything is lost, but some regulatory relief would be more than welcome”, said the founder of Gaming in Germany, Willem van Oort.
“As to the question whether German authorities foresaw these developments, some federal states, such as Hesse and Schleswig-Holstein, certainly did, other states not so much. Too often, legislators and regulators still underestimate how hard it is to effectively suppress online services compared to their physical counterparts. Relatively speaking, an illegal bar has a much, much harder time competing with its legal equivalent than an illegal online casino with a licensed operator”, added.

Dr. Joerg Hofmann, Senior Partner at Melchers Law, highlights the figures concerning operators in Germany. Licensed gambling operators in Germany are listed on the white list maintained by the GGL (‘Gemeinsame Glücksspielaufsichtsbehörde der Länder’). As of April 26, 2024, the list includes 30 sports betting operators, 39 online slot machine operators, and 5 online poker operators.
“This is a negligible number compared to the euphoria at the time when it was announced that Germany would introduce a licence regime. At that time, however, it was not yet known how restrictive the regulations for offers and advertising would be. Nor did anyone expect that Germany would introduce a gambling tax of 5% on stakes, which would significantly impair competitiveness. From October 2020 until the licence was issued, there was a transitional regime for online casinos, which had to adapt themselves and their products to the licensing provisions applicable from 1 July 2021 in order to obtain a licence. At this point, it was already apparent that numerous players were choosing offers that did not comply with the German restrictions. Operators who complied with the new regulations reported losses in turnover in the range of 60 to 80 per cent”, said in an interview with iGaming Express Dr. Joerg Hofmann, Senior Partner at Melchers Law.
“The GGL has now had the opportunity to observe these developments for the first few years. If they do not gloss over the situation with blinkers, they have the opportunity to counteract this in the upcoming first evaluation of experiences under the current Interstate Treaty on Gambling. However, I am only optimistic to a limited extent. Although I am very much aware of the growing expertise of the still relatively young authority, I also see that the necessary decision-making approaches of the qualified officials are still being thwarted politically. This is due to the involvement of the federal states. The GGL is not a federal authority. That, by the way, is its biggest problem”, added.
Main Issues of the German Market – Lack of Support for Legal Businesses
Restrictive regulations have led to an increase in the grey market. Many players, unwilling to comply with the new rules, have started using the services of illegal operators. The lack of proper oversight over this market segment has caused the grey market to grow dynamically.
As previously mentioned, the iGaming market in Germany includes a large number of active users, but only half of them play fully legally. This issue is one of the main challenges that the German government has to face.
Dr. Joerg Hofmann, Senior Partner at Melchers Law, in an interview with iGaming Express, pointed out that numerous regulations influence its growth. The renowned lawyer emphasized that the main issue in Germany is also the lack of support for licensed operators.
“In the field of gambling, any regulation is only as good as its ability to reach the players. The yardstick for assessment is the degree of channelling that can be achieved. If players opt for gambling offers outside the regulated market, the regulation is unsuitable. The grand plans for player protection and the intended strengthening of licensed operators have come to nothing. This is the core problem in Germany. The share of the black market in Germany is controversial and of course cannot be enumerated empirically.
Dr. Joerg Hofmann believes that the authorities are downplaying this fact, and the market faces a harsh reality every day. “From my consulting practice, I can say that the licensed operators have lost a massive part of their player base by adapting their offers to the licence regulations. Conservatively, I would say that this part is at least over 50 per cent.
“So what is the main challenge in Germany? It’s actually quite simple. The regulatory provisions must enable operators to offer a gambling offer that is sufficiently attractive to players. The player decides where to play. The licence holders must therefore be competitive. There is only one solution to this: the licence provisions based on the Interstate Treaty on Gambling must be reconsidered and adapted. Player protection will not be neglected in this process. On the contrary, more players will be reached. Responsible gambling can then be much more effective in its focus on monitoring gambling behaviour and any meaningful markers of harm,” summarized the Senior Partner at Melchers Law.
Other Problems of the German Market
According to Willem van Oort, the main problem in Germany is the country’s tax situation and the consequences of the 2021 treaty. “The main issue with the German market is that the 2021 Interstate Gambling Treaty is a political compromise that was designed to convince even the most gambling-adverse Länder to sign up for it. The tax situation – specifically, the 5.3% gambling tax on stakes rather than GGR – also does not help. These are very significant challenges that are baked in and would require significant political investment to change”, said the founder of Gaming in Germany.

According to Willem van Oort, there are various issues that could be resolved if the regulator took a somewhat more independent stance towards the German federal states. “At least some of the states tend to see the regulated market as something that ought to be kept in check rather than as a market that needs to do well in order to be a viable alternative to the black market”, added a renowned German gambling expert.
Player Freedom
The period from 2012 to 2021, during which the law was suspended, had very serious consequences. The biggest of these was the rise of the illegal gambling space, which gained significance among German players.
Furthermore, the lack of regulation for so many years has meant that current efforts to fix the situation are largely improvised. The introduction of numerous limits and bans may be an attempt to rectify years of neglect, but the effects of these actions are often negative.
The implementation of many restrictions has sparked a wave of criticism from players, who believe that the new regulations infringe on their freedom. They argue that they have the right to freely use gambling services, and excessive restrictions limit their possibilities. Many players emphasize that instead of introducing more restrictions, the government should focus on education and prevention.
Dr. Joerg Hofmann believes that betting and deposit limits make sense, but not in the current system in Germany. Our expert claims that the intentional approach to fighting addiction assumes that a uniform betting limit per player per month can protect them from addiction or financial ruin. Thus, it has been established that a player cannot deposit more than 1,000.00 EUR per month.
“This applies across all operators and is monitored centrally in real time by a server system. Exceptionally and under special conditions, this amount can be increased up to EUR 30,000.00. However, “one size fits all” does not apply to everyone. If players can easily afford higher deposits and higher stakes, what will they do? Migrate to the black market! High rollers in particular, who can be awarded up to 80 per cent of the betting stakes, will leave the licensed market if German regulation shows them a stop sign. So yes, the player’s freedom is massively affected when he plays in the regulated market. Their freedom is revived when they find their way out. But there is no state protection for them there. So there has to be a change of system here. Players must be free to decide on their own limits – just like in other countries. At the same time, however, the responsibility of the gambling operator must enable comprehensive monitoring that supervises player behaviour with regard to anomalies and takes appropriate measures to counteract the dangers of gambling”, said Dr. Joerg Hofmann.
The Senior Partner at Melchers Law, however, added that he disagrees with the notion that the numerous regulations are due to a desire to fix years of neglect. “Rather, it is a problem of choosing unsuitable means – unsuitable because they sound good in theory but drive players into the black market”, added.
Willem van Oort expressed a similar opinion. “Limited stakes are an obvious restriction on the freedom of players. Restricting players isn’t always bad, though. I can think of obvious examples of very unhealthy player behavior that should not be allowed. The question is, however, whether limiting stakes, in the way that German regulations mandate, is effective and proportionate. Personally, I don’t think so. Not least because the black market is never far away. That reality severely impacts the usefulness of one-size-fits-all approaches.
“I would be surprised if Germany’s limited stakes are a way to protect players after a significant period of neglect. I think it merely reflects the general idea that people, ideally, should not gamble at all. If they nonetheless must, they should only do so with very, very limited stakes. I get where these politicians are coming from, but it is just not how people work. Unfortunately, trying to change human nature – regardless of how well-intentioned one is – is a fool’s game in my experience”, said the founder of Gaming in Germany.
The German authorities therefore face many challenges in providing players with appropriate measures for responsible gaming while simultaneously ensuring that legal operators offer attractive solutions.
Currently, this situation in the German iGaming market does not look promising, leading to absurd court cases, such as those involving Betano and Tipico.
Betano’s Case
In 2018, a case began that could be groundbreaking for the German gambling industry. The Federal Court of Justice in Germany was ready to rule in favor of a player who sought to recover losses from an illegal sports betting operator in Germany, Betano.
Until recently, it appeared that another hearing would take place. However, on April 30, 2024, the Federal Court of Justice (Bundesgerichtshof) announced the cancellation of the hearing scheduled for May 2. The cancellation was due to a settlement reached by both parties.
The settlement could herald a wave of similar cases, further complicating the already turbulent landscape of the German gambling sector. After all, such a large company must have been aware of its limited chances in the dispute, leading to an agreement with the player.
Betano on the Defense. What is the Dispute About?
It dates back to 2018 when a player sought a refund of approximately €12,000 lost in bets placed with Betano, a subsidiary of Kaizen Gaming. The crux of the matter lies in the company’s status at that time. The player claimed that Betano did not have the required license, which would justify the reimbursement of losses.

In May 2023, the Higher Regional Court in Dresden sided with the player, prompting Betano’s parent company, Betkick Sportwettenservice GmbH, to file an appeal. The legal issue stems from the prolonged period of regulatory uncertainty in Germany, where the liberalization of the sports betting market was not supported by a functional licensing system, resulting in a legal vacuum.
Betano applied for a German sports betting license in 2012 and continued to offer betting services during the regulatory impasse, arguing that the responsibility for unregulated activity partly rested on delays in establishing a functioning licensing system. Nonetheless, the Federal Court’s opinion emphasized Betano’s non-compliance with German gambling regulations, particularly the failure to adhere to mandatory player protection measures such as the monthly betting limit of €1,000.
The court’s decision to issue a preliminary opinion before the final verdict was unusual and signaled an intention to move the case towards a clear legal resolution, preventing potential out-of-court settlements that could bypass the appeal process.
The Federal Court of Justice’s inclination to support the player in the Betano case marks a pivotal moment in the ongoing debate on gambling regulation and player protection in Germany. It underscores the urgent need for a consistent and enforceable regulatory system that protects players’ interests while providing clear operational guidelines for operators.
Impact of the Betano Case on Regulatory Policy
This case could influence future regulatory policies and legal proceedings in the German gambling industry. Ultimately, the parties reached an agreement, indicating a significant advantage for players in disputes with theoretically illegal operators.
“In these proceedings, there was ultimately no oral hearing before the Federal Court of Justice (Bundesgerichtshof) after the parties reached a last-minute settlement and the appeal was withdrawn. Nevertheless, the shortly before published reference order documents the preliminary assessment of the highest German civil court. If the court were to make a similar decision, an increased wave of lawsuits against sports betting operators could be expected. However, the assumptions underlying the reference order are incorrect and not tenable under the rule of law”, said the Senior Partner z Melchers Law, Dr. Joerg Hofmann.
“The Federal Court of Justice fails to recognise that the provision in the relevant Interstate Treaty that is decisive for the assessment of the possible nullity of gambling contracts, namely the prohibition of unlicensed betting events, was incompatible with the freedom to provide services under Art. 56 TFEU (as interpreted by the ECJ). The prohibition regulation, which restricts freedom in this respect, is therefore not only inapplicable in criminal and administrative law, but also in civil law. The Federal Court of Justice is attempting to use non-compliance with licence provisions, such as stake or deposit limits, as sufficient grounds for nullity on the grounds that the operator would have lost its ability to hold a licence in the event of corresponding violations. This is not tenable under the rule of law. This already ignores the fact that the limit regulations were still in need of implementation and were supposed to be implemented only in the licencing procedure, whereby an amount exceeding the general limit of EUR 1,000 per month could be set in the licence notification”, added.
Willem van Oort expressed his opinion on this matter. The founder of Gaming in Germany said: “As far as I can tell, it seems a bit surprising that an operator should have complied in detail with a sports betting regime that was indisputably not compliant with EU law. It would have been different if there had been a clear prohibition on sports betting at that time. Of course, there is also an argument to be made that any full ban on online gambling is not compliant with EU law. But that viewpoint is not generally accepted in legal circles. As far as consequences go, if Germany’s Federal Court of Justice ends up siding with the player, the main consequence will be that betting operators will be liable for reimbursing player losses in much the same way that casino operators already are”, stated.
As Willem van Oort mentioned, illegal online casinos should reimburse players for lost money. However, this is only in theory. In their latest rulings, German courts have consistently held online casino operators responsible for compensating players’ losses.
These rulings mandate that operators return the money lost by users, although in practice, these recommendations are not always enforced. The German court emphasized that operators should be held accountable for players’ losses, but many of them currently hide behind Malta’s Law No. 55, which provides them with legal protection against such enforcement.
Other online casino operators have opted for settlements with individual claimants, allowing them to avoid lengthy and costly court proceedings. Nevertheless, these actions pose many challenges for the German iGaming market. First and foremost, there is a need for more clear and effective legal regulations that will protect both players and operators.
The German iGaming market also faces the problem of the legality and regulation of foreign operators’ activities, which adds an additional burden to the national legal system. Therefore, the future of the iGaming industry in Germany requires significant changes and adaptations to meet new challenges and ensure safety and transparency in the online gambling market.
Another Bizarre Case – the Tipico Issue
A similar case to Betano is the Tipico issue. A player is trying to recover money wagered with an allegedly illegal operator. Interestingly, after both parties unanimously filed a motion to suspend the proceedings due to settlement negotiations, the original trial date was canceled. However, the parties reported the failure of the settlement negotiations and resumed the suspended proceedings. The new trial date is set for June 27, 2024.

The case will be referred to the CJEU, which pleased Tipico. In their official press release, it was stated that “they are clearly pleased with the fact that the District Court in Erfurt (LG Erfurt) in case 8 O 1125/123 wants to refer to the Court of Justice of the European Union (CJEU) questions regarding the admissibility of claims for reimbursement in online sports betting for the period before the license was issued, i.e., before October 9, 2020.”
Tipico argues that this strengthens their existing position. The operator claims that their clients in Germany have always used legal sports betting offers based on the European freedom to provide services and that there is no basis for reimbursements.
“According to the LG Erfurt’s decision, all questions regarding EU law in the field of online sports betting are to be referred to the CJEU. The court emphasizes that the CJEU has the final say in this matter,” reads the press release.
Are lawyers Exploiting the Situation and Designing a “New Business Model”?
Tipico treats this event as a clear signal to law firms that treat lawsuits against allegedly illegal bookmakers as a profitable business model. Tipico’s spokesperson, Matthias Folkmann, claims that in the case of reimbursement claims, players have been instrumentalized for years, and their ignorance and lack of experience are shamelessly exploited to support the business model of law firms and litigation funders and to maximize their own profits. The CJEU’s decision has the potential to ultimately deprive this business model of its foundation.
Tipico maintains that it operates in accordance with regulations and is a lawful provider. The operator intends to continue defending itself with all available means against the aforementioned business model.
“Another sports betting case has now been scheduled for an oral hearing before the Federal Court of Justice on 27 June 2024. Again, it concerns losses claimed by a player. It remains to be seen whether the court will change its opinion. Personally, I would not expect it to do so and am more confident that the European Court of Justice will correct the case law in Germany. This could happen soon. The Erfurt district court has announced that it will issue a corresponding order for reference. It continues to be exciting,” said in an interview with iGaming Express Dr. Joerg Hofmann, Senior Partner at Melchers Law.
What Does the Future Hold for the German iGaming Market?
The introduction of further, even more restrictive regulations may lead to serious consequences. More and more significant companies may decide to leave the German market, which will further weaken the legal gambling sector. As a result, the gray market will continue to grow, making it harder to control and increasing the risk for players.
The restrictions introduced in the German online gambling market were intended to protect players, but in practice, they have led to numerous problems. The growth of the gray market, absurdities arising from the new regulations, and criticism from players are just some of the consequences.
Ultimately, restrictive regulations may paradoxically contribute to the further development of the illegal market, which threatens both players and legal operators. It is essential to find a balance between protecting players and providing them with the freedom of choice to effectively manage the online gambling market in Germany.
Dr. Joerg Hofmann, Senior Partner at Melchers Law, believes that Germany needs a paradigm shift. “Gambling is still often treated in public and politically as if it were – to use the outdated and outmoded words of the Federal Constitutional Court from the 1970s – “undesirable”. However, if we take a realistic look at the eight-figure numbers of people who regularly and willingly participate in gambling, this is the wrong approach. Perhaps what is needed is a new generation of politicians, legislators and regulators who understand that this area also has its place in social life. And who understand that – apart from a few black sheep – this industry can be trusted and talked to. This already works very well in other countries. In Germany, we are at least seeing some initial positive changes.
“Current experience in the licensed market shows the urgent need for change. Legislation and regulation will not be able to ignore this. The hope that the black market can be effectively combated without making the licensed product attractive enough is long outdated.” Dr. Joerg Hofmann, however, remains optimistic. The Senior Partner at Melchers Law asserts that making the offerings of legal operators more attractive in the context of combating the gray market is only a matter of time.
Founder of Gaming in Germany, Willem van Oort, has limited his speculations regarding the German iGaming market. However, he acknowledged that operators benefit from the fact that the majority of their revenue comes from sports betting. “In a purely economic sense, online slots are a bit of a side activity. The German regulatory model for this vertical simply isn’t great, to say the least. This means, of course, that operators with strong betting offerings have a distinct advantage right now.”
Questions to the Regulator
In connection with journalistic integrity, we contacted the German regulator with a request for answers. After providing all the information they asked for, we did not receive a response.
We gave GGL two deadlines, which were certainly sufficient to provide answers to our pressing issues. Therefore, we include the mentioned questions below.
1. Are you planning to implement additional regulations to improve the German iGaming market in the face of current challenges? When can any actions be expected?
2. What are your thoughts on the Betano player’s case? Could his case lead to a wave of other cases that may end up in court?
3. Have the regulations introduced after the 2021 treaty brought the results you expected? What outcomes were you anticipating?
4. How, as a regulator, do you respond to the voices of some parts of society that numerous limits and regulations restrict the freedom of iGaming players in Germany?
